Pathophysiology
- Autoimmune mediated destruction of exocrine glands
- Classification
- Primary Sjogren’s
- Secondary Sjogren’s - rheumatoid arthritis, connective tissue disease
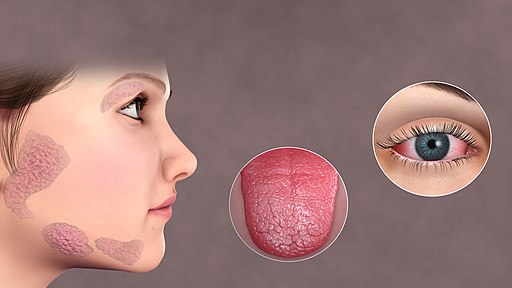
Clinical Features
- Epidemiology: Typically affects middle aged women
- Generalised features:
- Fatigue
- Diffuse, generalised joint pain
- Exocrine dysfunction results in:
- Keratoconjunctivitis Sicca - dry eyes - a foreign body, gritty sensation and light sensitivity
- Dry mouth - xerostomia - difficulty chewing, swallowing or talking.
- Increased risk of oral candidiasis
- Parotitis - facial swelling
- Vaginal dryness
- Photosensitive rashes
Complications
- Lymphoid malignancy ( x 50 risk)
- Secondary Raynaud's syndrome

Investigations
Antibodies
- Rheumatoid factor - 50% positive
- ANA - 70% positive
- ANTI-Ro (SSA) - 70% Primary SS
- Anti-La (SSB) - 30%
Other investigations
- Schirmer’s test - reduced tear film (<5mm after 5 minutes)
- Labial (lip) salivary gland biopsy - histology -l focal lymphocytic infiltration
- Anti-Ro/La positive
Management
- Dry eyes and mouth - pilocarpine, artificial tears
