Dermatomyositis
Dermatomyositis is an inflammatory condition resulting in symmetrical proximal muscle weakness and skin lesions.
- Dermatomyositis is idiopathic in most cases.
- However, it is important to note that it may indicate an underlying malignancy in as many as 25% of patients - ovarian, breast, lung
Clinical features
Cutaneous features - 'Dermato...'
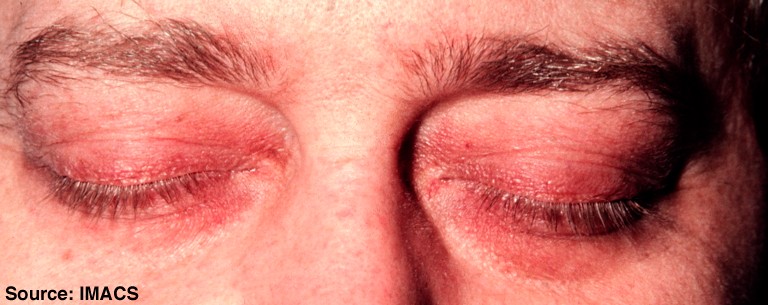
- Heliotrope periorbital rash - redish/purple rash on eyelids
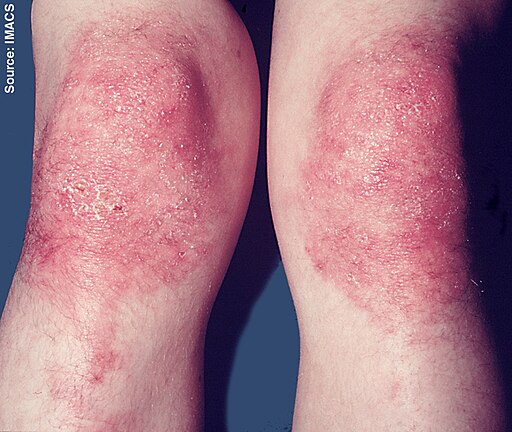
- Red macular rash affecting back and shoulders
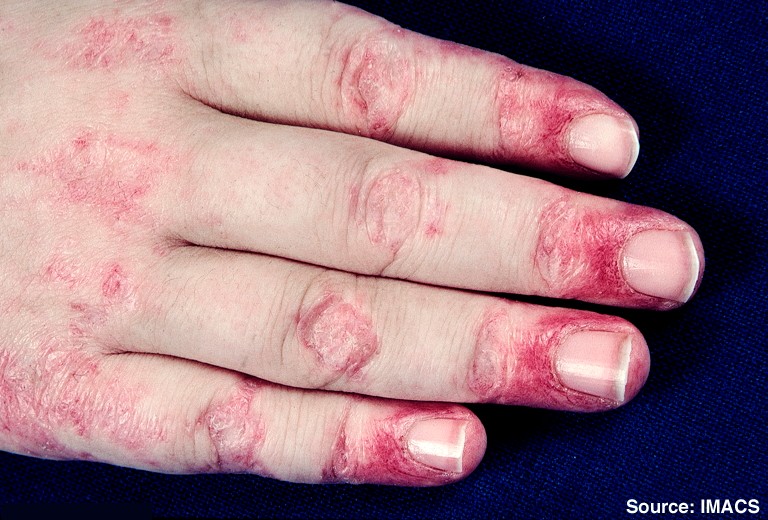
- Mechanics hands – Gottron’s red papules on extensor surfaces - often overlying the knuckles and PIP/DIP joints
- Rashes are photosensitive
‘Myositis..’
- Symmetrical, proximal weakness +/- tenderness
- Difficult climbing stairs, getting up from chair, holding up a cup of tea or brushing hair etc.
General symptoms
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
- Night sweats
Other features: ILD causing shortness of breath, Raynaud’s phenomenon
Investigations
Bloods
- Raised CK due to myositis
- ANA positive (80%)
- Antibodies:
- Anti-MI-2 Antibodies
- Anti-SRP antibodies
- (Anti-Jo 1 antibodies - more associated with polymyositis)
Management
- Steroids - Prednisolone
- Patients should be screened for malignancy
Polymyositis
- A variant of dermatomyositis without skin manifestations
- Clinical features:
- Symmetrical, proximal weakness +/- tenderness
- Difficult climbing stairs, getting up from chair, holding up a cup of tea or brushing hair etc.
- Symmetrical, proximal weakness +/- tenderness
- Investigations:
- Raised CK due to myositis
- Antibodies: Anti-JO1 (vs histidine tRNA ligase)
