Mixed Connective Tissue Disease / Sharp's Syndrome
Pathophysiology
- A multisystem autoimmune disease with mixed features of SLE, systemic sclerosis and myositis.
Clinical Features
- Myalgia
- Shortness of breath due to pulmonary hypertension
- Polyarthralgia
- Raynaud's phenomenon
- Dactylitis "sausage fingers"
- Rash
- Oesophageal dysfunction / swallowing difficulties
- Renal/CNS disease is unlikely
Antibodies
- Anti-U1 ribonucleoprotein antibodies (Anti-RNP)
Management
- DMARDs
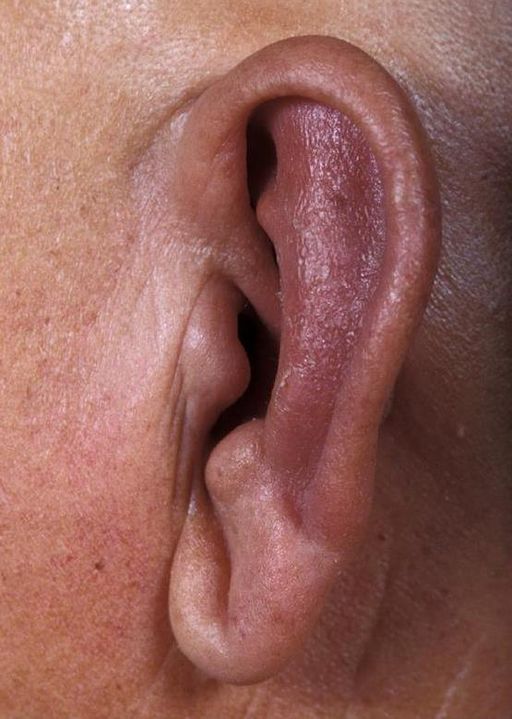
Relapsing Polychondritis
Pathophysiology
- Episodic inflammation of cartilage, particularly of the ears, nose, joints
Clinical Features
- Ears - Auricular chondritis, hearing loss, vertigo
- Nose - nasal chondritis - saddle nose
- Respiratory tract - hoarse voice, aphonia, wheeze
- Joints - arthralgia
Management
- Steroids can be used to induce remission
- Maintenance - DMARDs
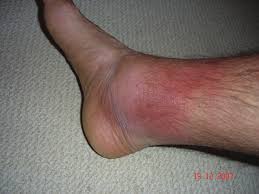
Familial Mediterranean Fever
Pathophysiology
- An autosomal recessive disease resulting in recurrent episodes of acute polyserositis
Epidemiology
- Increased prevalence in patients of Turkish, Armenian, Arabic descent
Clinical features
- Patients have 'attacks' lasting 1-3 days with symptoms including:
- Fever
- Pleurisy
- Abdominal pain, peritonitis
- Pericarditis
- Arthritis
- Erysipeloid rash on the lower limbs
Management
- 1st line - colchicine
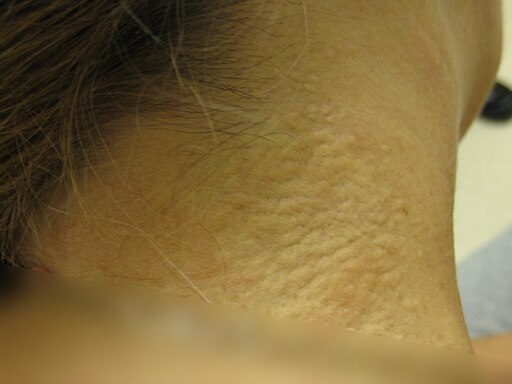
Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum
Pathophysiology
- An autosomal recessive disease caused by calcium deposition and mineralization of the elastic fibres of connective tissues around the body.
Clinical Features
- Retinal angioid streaks - red bands radiating from the disc.
- 'Plucked chicken skin appearance'
- Small yellow papules in a liner pattern, in groups forming plaques
- Loss of elastic tissue and saggy looking skin in neck, axilla etc.
- Cardiovascular complications:
- Intermittent claudication is a common early sign of arterial disease
- Ischaemic heart disease
- MV valve prolapse
- Gastrointestinal bleeding - melaena/frank bleeding/occult in stool
Adult-onset Still’s Disease
Pathophysiology
- A systemic autoimmune disease
Clinical features
A triad of:
- Fever
- Joint pain - especially the knees, wrists and ankles
- Maculopapular salmon rash
- Other - lymphadenopathy, sore throat, hepatosplenomegaly, myalgia, pericarditis.
Investigations
- No single diagnostic test - Ferritin, ESR and CRP elevated
- Autoantibodies: Rheumatoid factor and ANA are negative
Management
- 1st Line: NSAIDs and corticosteroids
- NSAIDs for symptomatic control
- Once diagnosis is confirmed patients can be treated with steroids
- Long term: DMARDs - Methotrexate
- Alternatives: ciclosporin, leflunomide, azathioprine, MMF, cyclophosphamide
- Alternative: If failure of 2 DMARDs, Anakinra (IL-1 receptor antagonist) is recommended by NICE
